Introduction
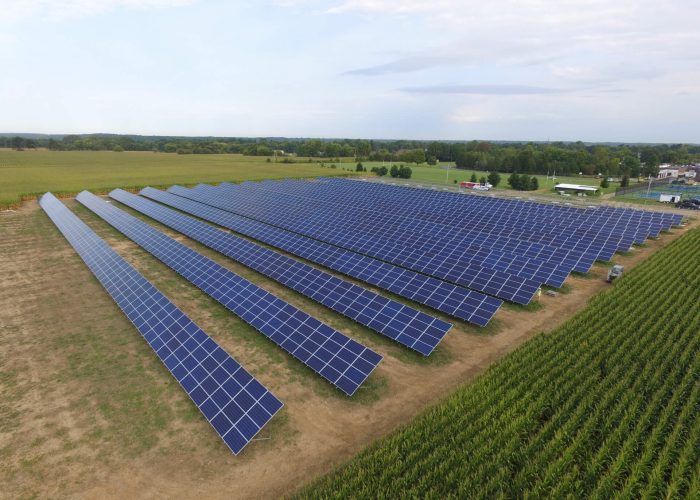
Solar is helping building owners become more resilient, reduce utility costs, and fight climate change. And its demand is booming. In the last decade alone, solar power has grown at an average annual rate of 24%! But with this growth comes a need for more and more land to accommodate the growing number of solar panels. Instead of covering that land with gravel, an innovative solution, solar pollinator fields, will make solar more sustainable while offering immense benefits to the pollinators our ecosystem relies upon.
In this article, I’ve answered common questions I’ve heard about solar pollinator fields and how they can transform our solar landscapes with biodiversity.
What Are Solar Pollinator Fields?
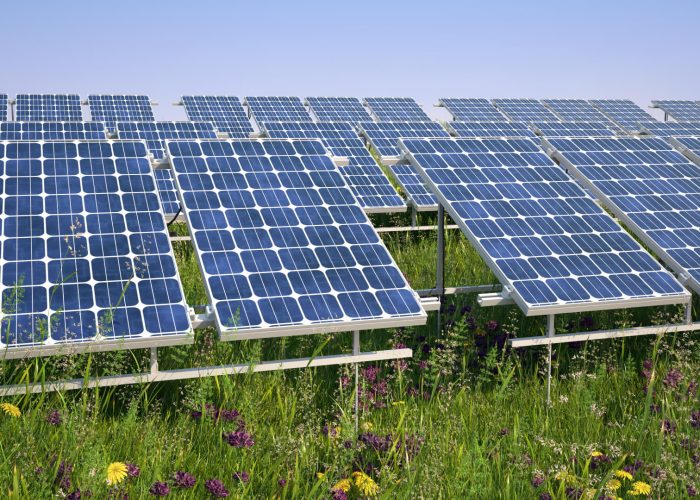
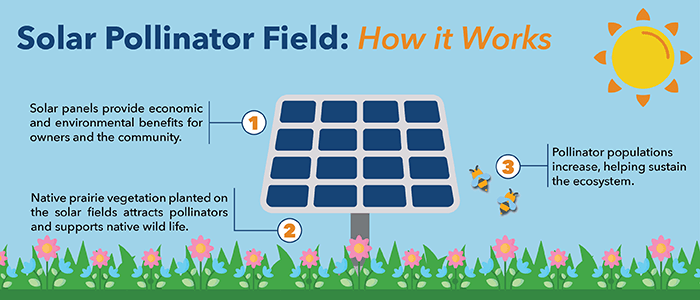
Solar pollinator fields are a specialized type of solar installation designed to support renewable energy generation and the promotion of biodiversity. Unlike traditional solar farms, which often involve vast areas of photovoltaic panels installed on clear land, solar pollinator fields integrate native, pollinator-friendly plant species in the spaces between and around the panels. This native vegetation creates a safe habitat for pollinators, butterflies, birds, and small prairie animals to thrive.
Solar pollinator fields aim to address environmental challenges by mitigating their impact on ecosystems that lead to declining pollinator populations while still producing clean, renewable energy. These innovative installations offer a sustainable and multifunctional land-use approach that benefits energy production and local biodiversity.
The main components of a solar pollinator field include:
- Solar Panels: The primary purpose of the installation is to generate electricity. In a pollinator field setting, they are usually mounted on structures to allow plenty of space around and between them for native vegetation, light for plants, and access for maintenance.
- Native Plants: Wildflowers, grasses, and other vegetation native to the region are strategically planted within and around the solar arrays to create a pollinator-friendly habitat. Various native seed mixes can be tailored with low-growing and multi-season species to encourage pollination opportunities throughout the year.
- Pollinator Habitats: The fields are designed to attract pollinators, as they play a crucial role in fertilizing plants, including our food crops. These habitats include nesting sites, water sources, and food sources like nectar and pollen.
How Do You Maintain a Solar Pollinator Field?
Maintaining a solar pollinator field is essential to ensure the longevity of both the solar panels and the biodiversity-promoting aspects of the site. While the specific maintenance requirements may vary depending on the location, climate, and the types of plants and pollinators involved, here are some generalized maintenance practices:
- Regular Inspection of Panels: Periodic inspections of the solar panels and supporting structures are crucial to identify any issues or damage. This includes checking for loose connections, physical damage, or dirt buildup on the panels.
- Vegetation Management: Managing the native plants is a significant part of maintenance. It involves regular weeding and controlling the growth of invasive species. You’ll want to prevent any single plant species from dominating the area and ensure a diverse range of native plants for pollinators.
- Mowing: Controlled mowing can help maintain the desired height and density of the vegetation. It should be done at specific times to avoid disturbing pollinators during their active periods.
- Pest Control: Avoid using pesticides or herbicides in the solar pollinator field, as these can harm native plants and pollinators. Instead, implement natural pest control methods or consider introducing beneficial insects for pest management.
- Nesting Sites: Maintain and protect nesting sites for pollinators, such as bee boxes, to encourage their presence and nesting in suitable structures instead of solar panels.
What are the Benefits of Solar Pollinator Fields?
Solar pollinator fields represent an innovative and sustainable approach to energy generation that aligns with ecological and conservation goals. Additional benefits include:
- Renewable Energy Generation: Solar pollinator fields harness the power of the sun to generate clean, renewable electricity. They contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
- Biodiversity Support: By incorporating native plants and creating habitats for pollinators, these fields actively promote biodiversity. They provide essential food and shelter for bees, butterflies, birds, and other wildlife, helping to counter the decline in pollinator populations.
- Pollination Services: Pollinators play a vital role in the reproduction of many plants, including crops. Solar pollinator fields enhance local pollination services, leading to higher crop yields and better food security.
- Habitat Restoration: These fields can help restore natural habitats and ecosystems that may have been disrupted by conventional agriculture or development. They can act as a refuge for native plants and wildlife.
- Erosion Control: The root systems of native plants in solar pollinator fields help prevent soil erosion, enhancing soil stability and water quality.
- Aesthetic Value: Solar pollinator fields create visually appealing landscapes integrating technology and nature. They contribute to the beautification of the environment.
- Community Engagement: These fields often engage local communities in ecological and conservation efforts. They serve as educational tools and offer opportunities for public involvement in environmental initiatives. For example, they are offering new options for FFA Programs with the rise of agrivoltaic projects.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: The presence of native plants can reduce maintenance costs compared to conventional solar installations because they may require less mowing and weed control.
- Sustainable Land Use: Solar pollinator fields optimize land use by combining energy production with conservation efforts, demonstrating a harmonious coexistence between technology and nature.
Related Reading: Solar is More Environmentally Friendly than Your Blue Jeans
Why Does it Matter?
Pollinators play a pivotal role in the agricultural industry, with an estimated 35% of global crop production dependent on them. This influence extends beyond farming, significantly impacting the overall economy as well. They are the unsung heroes behind the pollination of various crops that provide us with food, beverages, textiles, plant-based medicines, and more.
Sadly, many pollinators are now under threat due to habitat loss, pesticide exposure, inadequate nutrition, diseases, and dwindling genetic diversity. As we allocate increasing amounts of land to solar farms, it becomes economically prudent to prioritize sustainable ecological practices. By bolstering the well-being of local pollinators, the incorporation of native pollinator-friendly vegetation not only aids crop production but also elevates the visual appeal of solar arrays, creating a win-win scenario for both nature and industry.
Is a Solar Pollinator Field Right for My Solar Project?
Remember that the decision to implement a solar pollinator field is significant, with implications for the environment, energy generation, and your local community. Careful consideration and planning ensure the project aligns with your goals and values. Public owners must weigh the environmental impact, permitting requirements/regulations, cost/benefit, and long-term commitment to maintaining the natural vegetation.
If this seems like a great solution for your school or city, the next step is selecting a qualified solar provider for the design and installation. Performance Services is a NAESCO-accredited design-builder. We have in-house solar engineers and project managers who can design, install, and monitor the right-sized solar solution for your needs. Learn more about our comprehensive solar process.
Related Reading: Solar Power: Practical, Reliable, and Affordable for Public Entities
Conclusion
The synergy between solar energy generation and biodiversity support is the key to how solar pollinator fields work. They help combat habitat loss, provide essential pollination services, and produce renewable energy all in one sustainable package. It’s a win-win approach for a greener and more biodiverse future.
Related Reading: Myth vs. Fact: Top 10 Misconceptions about Solar Power
Are you ready to contribute to a sustainable future with a solar pollinator field? Contact us today, and our solar experts will work with you to design, right-size, and install solar that will offset your electricity consumption and provide a haven for essential pollinators.





